How does polysomnography ? work
Polysomnography is the best-known method for examining sleep disorders and is carried out in special sleep laboratories. We explain here what happens during polysomnography and how it helps to identify sleep problems.
Table of contents
- What is polysomnography?
- How does polysomnography work?
- How does polysomnography work?
- Who needs polysomnography?
- Conclusion
1. What is polysomnography?
Polysomnography (PSG) is a method for examining sleep in which various biological parameters are measured during sleep and then evaluated. This allows sleep behavior to be comprehensively examined on a physiological level and provides information about the time it takes to fall asleep, interruptions in sleep, and other abnormalities. This can help identify sleep problems, especially those with organic causes - for example, movement disorders or breathing pauses (sleep apnea).
2. How does polysomnography work?
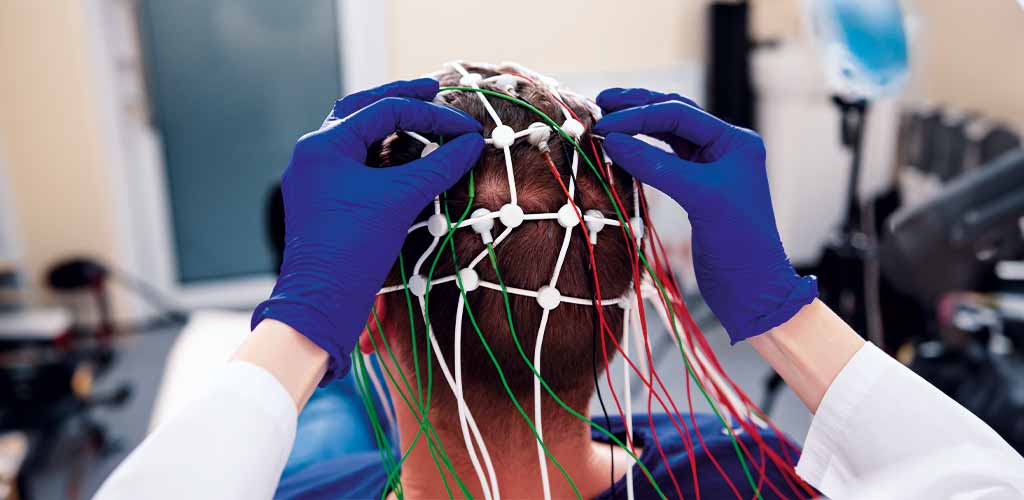
During sleep, the entire body function changes, which is why polysomnography collects a lot of different information that can then be put together to create the clearest possible picture. Brain waves, eye movements, heart and respiratory function, and muscle activity are measured and recorded during sleep using well-known medical procedures (ECG, EEG, etc.).
This allows the body to be examined in its entirety during sleep, which will reveal sleep problems and potential causes. For example, you can find out whether the patient has a healthy sleep structure and all sleep phases runs through or moves unusually at night.
These parameters are recorded during polysomnography:
- brain waves using EEG (electroencephalicography)
- Eye movement using EOG (electrookulography)
- Muscle tension tone using EMG (electricmyography)
- heart rate and heart rhythm using ECG (electrocardiograms)
- body temperature
- respiratory flow and respiratory movement
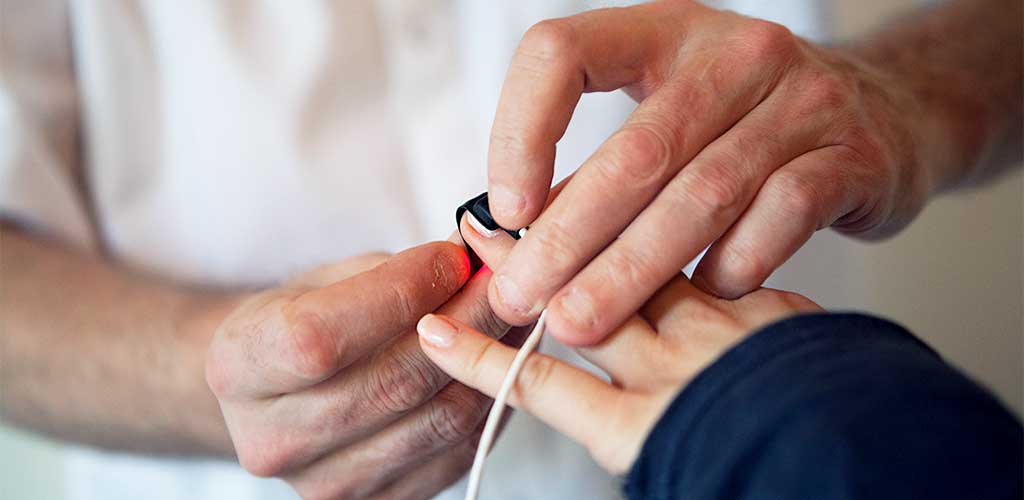
- oxygen content in the blood
- leg movement
- body position
3. How does polysomnography work?
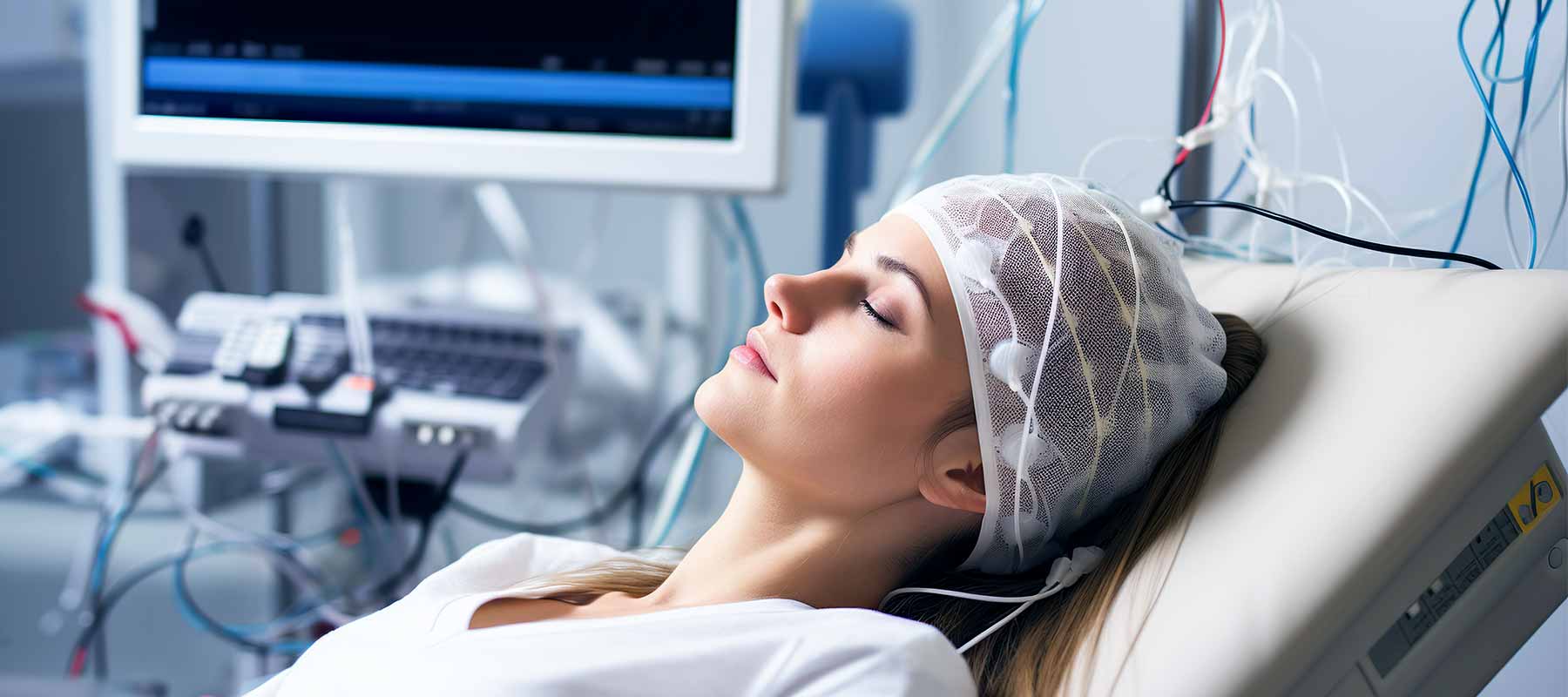
The examination is quite comprehensive and usually takes place under observation in a sleep laboratory. However, there is also the option of an outpatient screening at home beforehand, a so-called polygraphy. The patient is given a small device to take home that monitors pulse rate, blood oxygen saturation and respiratory function overnight. A polygraphy is often the first step in identifying sleep problems. If abnormalities are found, an inpatient polysomnography in the sleep laboratory often follows. There, trained staff will look after the patient overnight.
The patient spends the night in the sleep laboratory in a monitored single room. There he prepares for sleep as usual and is then connected to all monitoring devices. For this purpose, many small electrodes (sensors) are stuck directly to the skin on the head and the rest of the body. They are connected by cables to a portable measuring device so that the patient remains mobile at night and can, for example, go to the toilet without disconnecting the electronic connections.Once all preparations have been made, the staff leaves the room, goes to the monitoring room and the patient can lie down in bed and sleep.
The next morning, all electrodes are removed and the results of the examination are evaluated. These are then often discussed in a separate appointment.
4. Who needs polysomnography?
Polysomnography is usually considered when serious sleep disorders exist and outpatient diagnostic procedures do not provide sufficient information.
Polysomnography is often used for …
- sleep apnea (nighttime breathing pauses) and other breathing problems
- insomnia (Persistent difficulty falling asleep and staying asleep)
- narcolepsy (sleep attacks & drowsiness)
- Restless Legs Syndrome (RLS) and other movement disorders
- Unusual behavior, e.g. REM sleep disorder, sleepwalking
Whether a sleep laboratory examination is necessary is usually decided by the family doctor or ENT doctor.
5. Conclusion
-
Polysomnography is a procedure for examining sleep in order to identify sleep disorders and their causes.
-
Polysomnography involves analyzing brain activity, heart and respiratory function, eye movement and many other physiological parameters using electrodes and measuring devices.
-
Polysomnography takes place in a sleep laboratory and is suitable for people who suffer from sleep disorders such as sleep apnea, insomnia or RLS.
Best regards and see you soon!




Leave a comment
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.